Journey into the realm of cell biology with our comprehensive guide to cell membrane structure and function worksheet answers. This exploration unveils the intricate workings of the cell membrane, a vital gateway that governs cellular life and holds profound implications for human health.
Our discourse delves into the composition of the cell membrane, deciphering the roles of phospholipids, embedded proteins, and carbohydrates. We elucidate the mechanisms by which molecules traverse this selective barrier, unraveling the secrets of cellular homeostasis and regulation.
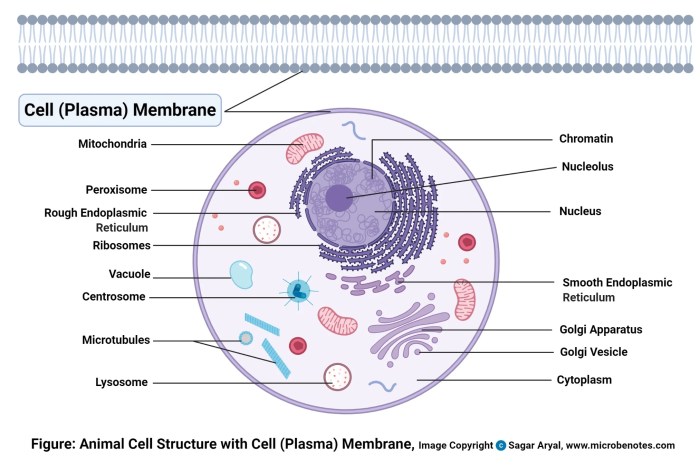
Cell Membrane Structure
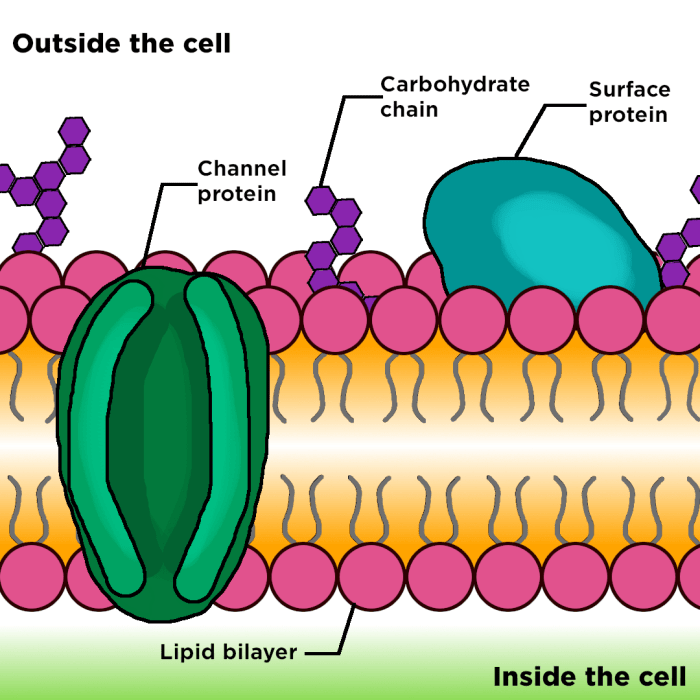
The cell membrane, also known as the plasma membrane, is a thin layer that surrounds all cells. It acts as a barrier between the cell and its surroundings, protecting the cell from its environment and regulating the movement of substances into and out of the cell.
Composition of the Cell Membrane
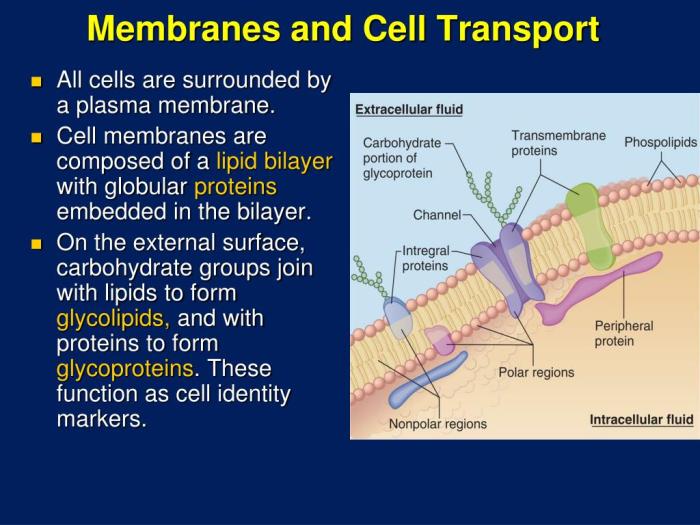
The cell membrane is composed of a phospholipid bilayer, a double layer of phospholipids. Phospholipids are molecules that have a hydrophilic (water-loving) head and a hydrophobic (water-hating) tail. The hydrophilic heads face outward, interacting with the aqueous environment, while the hydrophobic tails face inward, forming a nonpolar core.
Embedded within the phospholipid bilayer are proteins, which perform a variety of functions, including transport, signaling, and cell adhesion.
Types of Embedded Proteins, Cell membrane structure and function worksheet answers
There are two main types of embedded proteins: integral proteins and peripheral proteins. Integral proteins are embedded in the phospholipid bilayer, spanning the entire membrane. Peripheral proteins are attached to the surface of the membrane, either on the cytoplasmic or extracellular side.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Phospholipids | Form the lipid bilayer, providing a barrier between the cell and its surroundings |
| Integral proteins | Embedded in the phospholipid bilayer, spanning the entire membrane; responsible for transport, signaling, and other functions |
| Peripheral proteins | Attached to the surface of the membrane, either on the cytoplasmic or extracellular side; involved in cell adhesion and signaling |
| Carbohydrates | Attached to proteins or lipids on the extracellular side of the membrane; involved in cell recognition and adhesion |
Detailed FAQs: Cell Membrane Structure And Function Worksheet Answers
What is the primary function of the cell membrane?
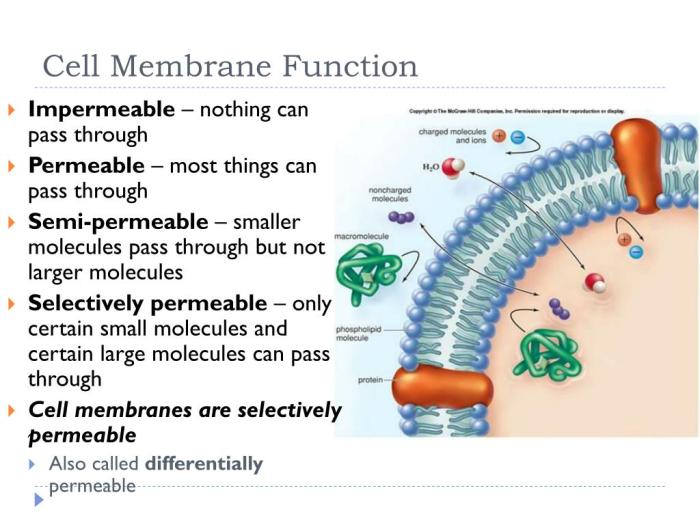
The cell membrane serves as a selectively permeable barrier, regulating the entry and exit of substances into and out of the cell, maintaining cellular homeostasis.
How do molecules move across the cell membrane?
Molecules traverse the cell membrane through various mechanisms, including passive diffusion, facilitated diffusion, active transport, and endocytosis/exocytosis.
What are the consequences of cell membrane defects?
Defects in the cell membrane can lead to a range of diseases, including cystic fibrosis, sickle cell anemia, and certain types of cancer.